
Nowadays, the development direction of smart cars has become an industry consensus, and in the field of intelligence, the popularity of autonomous driving has always been high. The wire-controlled chassis is called the cornerstone of autonomous driving, and as autonomous driving continues to heat up, the spring of wire-controlled chassis has quietly arrived. In fact, at this stage, the wire-controlled chassis has become the key focus of many traditional first-tier suppliers, and both traditional brands and new car forces are extremely enthusiastic about the wire-controlled chassis.

The essence of wire-controlled chassis is to transform the signal conduction mechanism of the car chassis into wire control, replacing mechanical signal conduction with electrical signal conduction. Its core feature is the ability to achieve “decoupling” between the actuator and the operation structures controlled by the driver, such as the steering wheel and brake pedal. Specifically, the conduction process of wire-controlled chassis transmits the driver’s operational commands in the form of electrical signals to the controller, which then issues instructions to the corresponding actuator, ultimately enabling the actuator to perform functions such as steering, braking, and driving. In simple terms, the fundamental change of wire-controlled chassis is the replacement of the traditional mechanical connection between the vehicle’s steering wheel, pedals, and the chassis with a wire-controlled structure, transforming the overall mechanical system directly controlled by human power into two independent parts composed of the operating end and the equipment end. Based on this, the equipment end can not only receive signals from the driver, but also receive electrical signal operations from other sources, laying the foundation for fully automated driving.
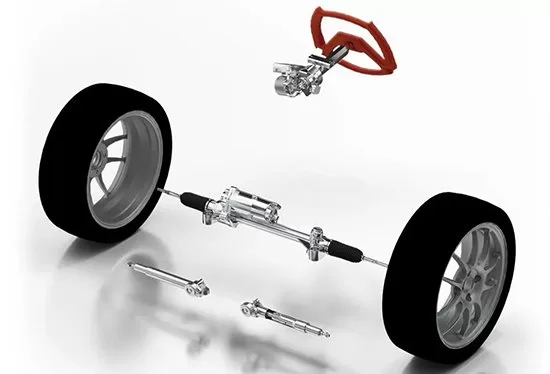
1. The steer-by-wire system is mainly composed of the steering wheel module, main controller, actuator module, fault handling system, power supply, etc. The steering wheel module, main controller, and actuator module are the three main parts of the steer-by-wire system, while other modules are auxiliary systems. When the driver turns the steering wheel, the angle sensor and torque sensor of the steering wheel will measure the angle and torque information and convert it into electrical signals, which are then transmitted to the main controller. At the same time, the main controller will also receive the wheel motion status signals collected by corresponding sensors, such as vehicle speed, longitudinal acceleration, lateral angular velocity, etc. Based on the transmission and reception of all the above electrical signals, the main controller will analyze and process the steering wheel angle and torque signals, and then send instructions to the steering actuator motor to complete the steering. 2. The throttle-by-wire system is essentially the “electronic throttle”, which replaces traditional throttle cables or rods with electrical signals. When the driver presses the throttle, the pedal position sensor will transmit the sensed signal to the ECU, which will then analyze and judge the signal before sending instructions to the drive motor. It is important to note that this drive motor directly controls the throttle opening, allowing it to adjust the flow of combustible mixture. In contrast to traditional throttle cables, which cannot control the “air-fuel ratio” and have a direct and rigid connection between the throttle and the pedal, the throttle-by-wire system allows for the adjustment of the throttle to the optimal position, achieving as close as possible to the theoretical “air-fuel ratio” under different loads and conditions. 3. Brake-by-wire system
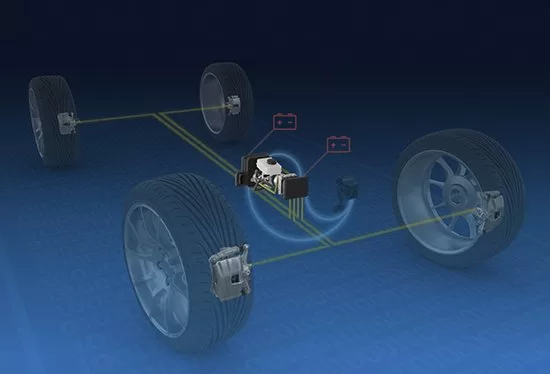
1. The working mode of wire-controlled braking is similar to that of wire-controlled throttle, both of which aim to minimize mechanical connections and separate the power transmission between the pedal and the controller. Wire-controlled braking uses a brake pedal position sensor to monitor the opening of the brake pedal, converting the mechanical signal of the pedal into an electronic signal, and then transmitting it to the control system and actuator to release the braking force. In addition, it also simulates the damping effect of the brake pedal based on certain software algorithms and feeds it back to the driver. Generally, if the brake pedal is only connected to a brake pedal position sensor and there is no rigid or hydraulic connection between the pedal and the braking system, it can be considered a wire-controlled braking system. 2. Shift By Wire The full name of the wire-controlled shifting system is “Shift By Wire.” Its appearance breaks the limitation of the traditional shift lever having to be hard-connected to the gearbox, and it does not require any mechanical structure, only using an electronic control system to achieve transmission. Compared to traditional shifting mechanisms, wire-controlled shifting, without the constraint of cables, can make the entire system lighter, smaller, and smarter. The wire-controlled shifting is mainly composed of a shift lever and a sensor control unit. When the driver selects a gear, the sensor will transmit the operation request to the gearbox control unit through an electronic signal. It will then analyze the vehicle’s current status, such as engine speed, vehicle speed, and throttle opening, and then make a judgment based on the communication protocol to determine whether to execute the shifting request. If everything is correct, the TCU will send a command to the corresponding solenoid valve inside the gearbox to switch gears. If there is a misoperation, such as forcefully shifting into reverse while driving at high speed, the TCU will make an intelligent judgment and if it is deemed an unsafe abnormal operation, it will not send a command to the gearbox, showing great intelligence. 3. Wire-Controlled Suspension
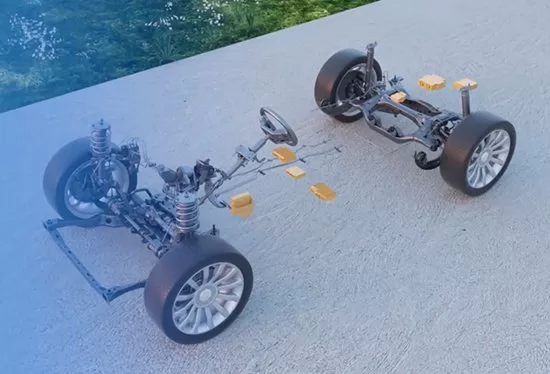
The car suspension system consists of elastic components, shock absorbers, steering mechanisms, and stabilizers. In contrast, the wire-controlled suspension system mainly consists of wire-controlled springs, wire-controlled shock absorbers, and wire-controlled anti-roll bars. It can automatically adjust the height, stiffness, and damping of the suspension according to the actual road conditions, thereby achieving fine control of the driving posture. The wire-controlled suspension control system is essentially a closed-loop adaptive control system that can meet the compatibility requirements of comfort and handling under different operating conditions. The wire-controlled suspension uses active or semi-active elastic components, which are helped by sensors to identify the vehicle’s driving status. The processor processes and outputs different elastic characteristics, and the wire-controlled method is used to execute the elastic component system, thereby achieving comfortable or sporty suspension characteristics. Active suspension systems can bring better driving safety and comfort, and in the era of intelligence, they have become a new development trend.