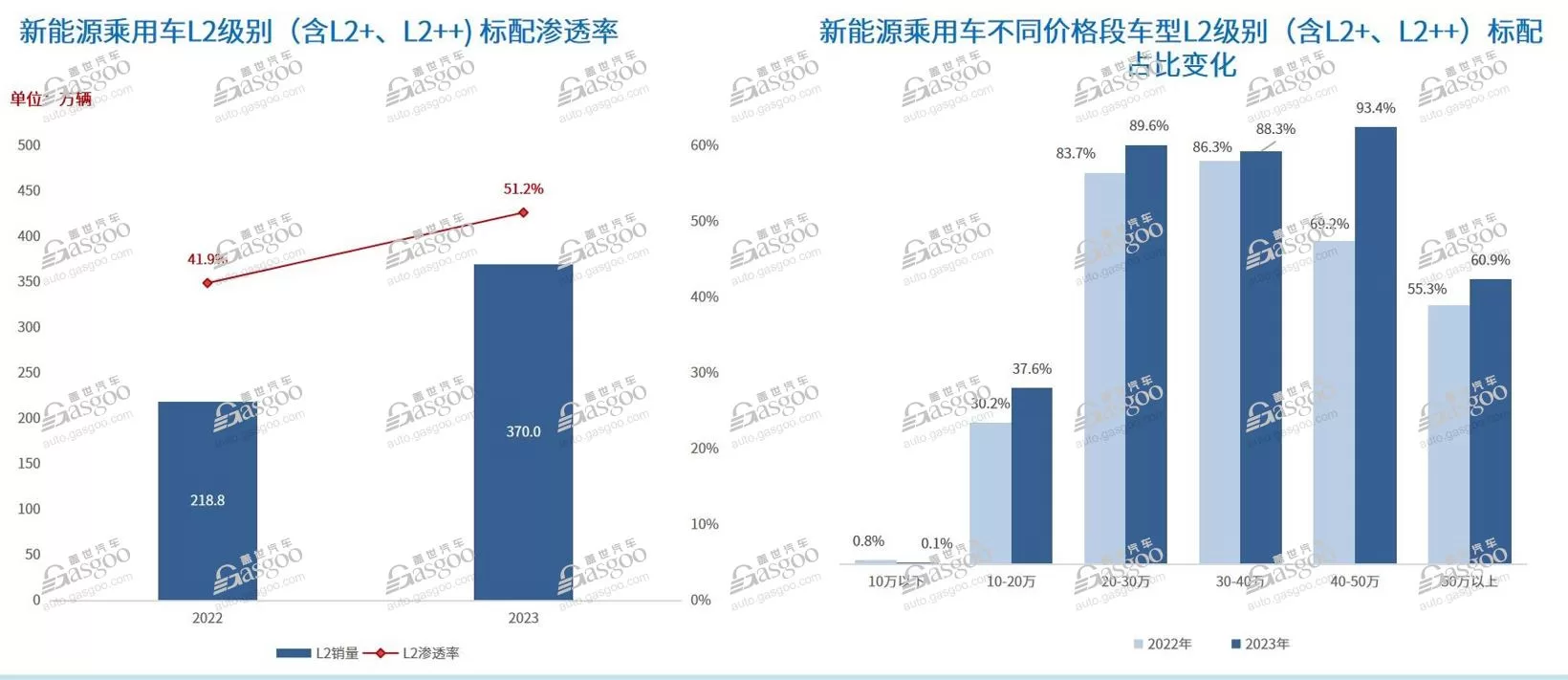
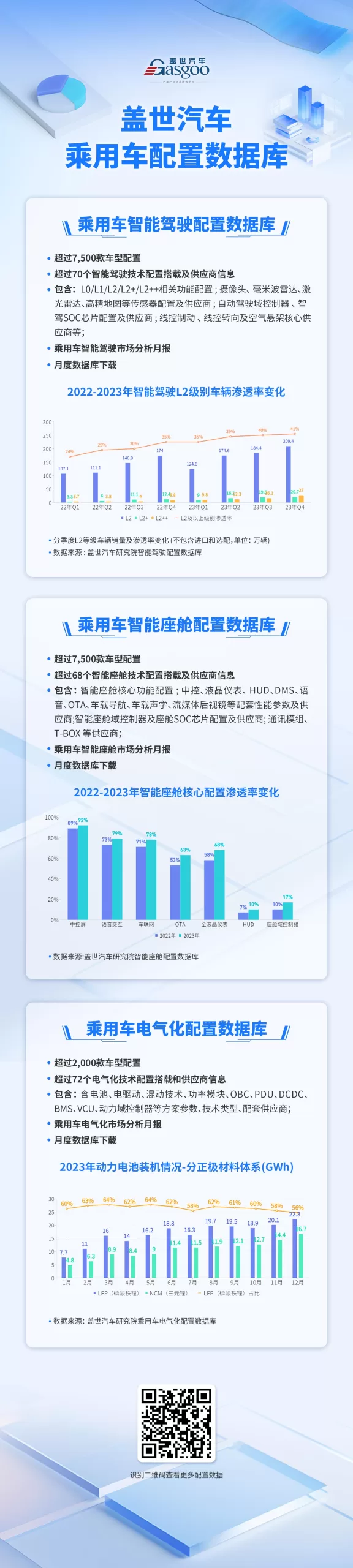
On March 29, 2024, the “China Automotive New Supply Chain Configuration Data Product Launch Conference” hosted by the World Automotive Research Institute was successfully held in Shanghai. The World Automotive Research Institute aims to be a leading think tank in the automotive industry, focusing on intelligent insights into the entire automotive industry chain through core data resources such as automotive supply chain configuration information and vehicle sales volume information, and providing comprehensive research results and complete industry data resources to support industry users in making business decisions. At this China Automotive New Supply Chain Configuration Data Product Launch Conference, we introduced and released three sets of original database products: Passenger Car Intelligent Driving Configuration Database, Passenger Car Intelligent Cabin Configuration Database, and Passenger Car Electrification Configuration Database, along with market analysis monthly reports. Currently, autonomous driving technology is rapidly advancing, from basic vehicle control assistance to advanced autonomous driving assistance, and from simple functions to highly integrated and intelligent complex systems. The L2 level driving assistance penetration rate is rapidly increasing, and the hot market for urban NOA, along with the introduction of high-level autonomous driving-related policies, is driving a new round of rapid development for China’s local intelligent driving solutions and suppliers. The penetration rate of L2 level driving assistance is rapidly increasing, and urban NOA is accelerating its implementation. ADAS continues to enhance the importance of vehicle safety, with the 2024 version of C-NCAP optimizing and upgrading existing scenarios based on the 2021 version, modifying and updating test parameters, and adding multiple active safety test items. As the performance of functions such as lane-keeping assistance and full-speed adaptive cruise control continues to improve, and the cost reduction brought about by mass production and technological improvements allows more models to offer driving assistance functions at lower prices, especially in the price range of 100,000 to 200,000 RMB, becoming the main market for L2 level driving assistance. According to the World Automotive Research Institute’s Intelligent Driving Configuration Database, the standard configuration volume of L2 level new energy passenger cars in the market reached 3.7 million units in 2023, with a market penetration rate exceeding 51%. Among them, the penetration rate of models in the 200,000 to 500,000 RMB price range has already exceeded 85%.
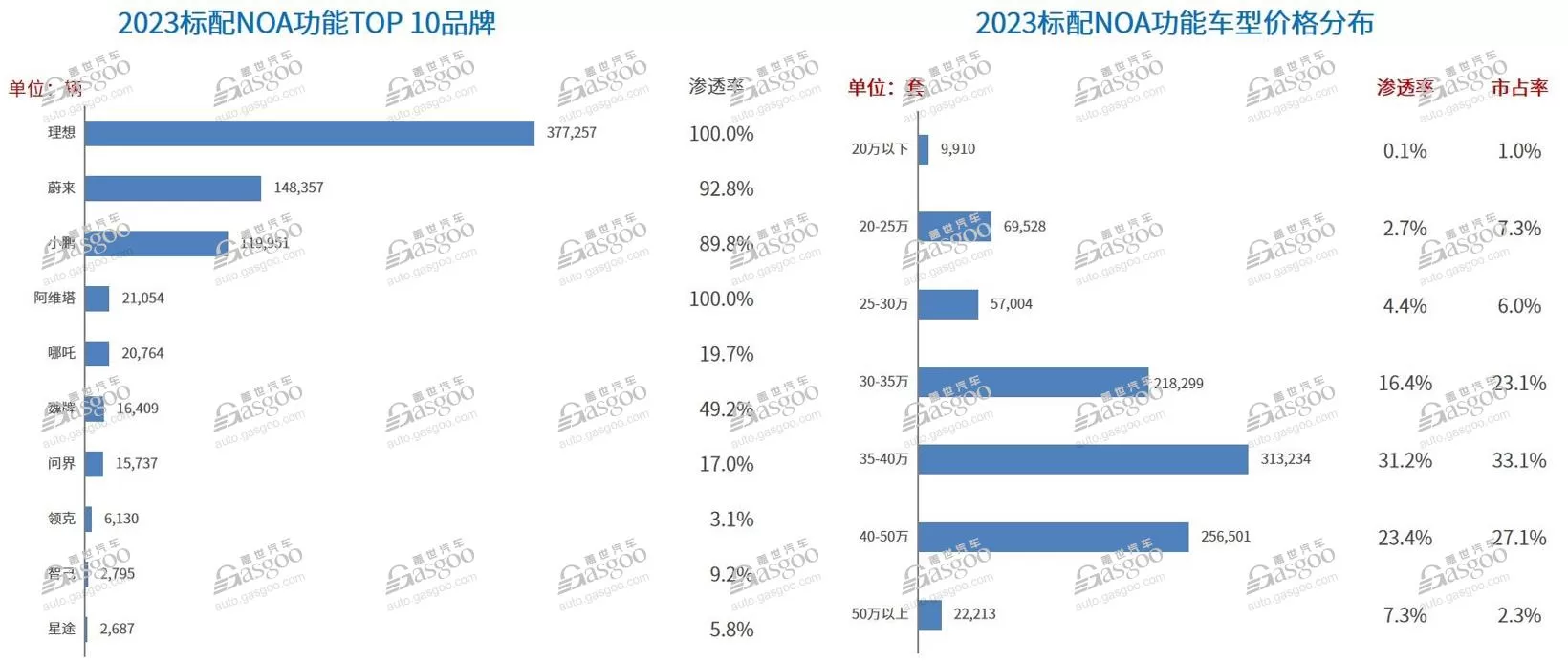
As the penetration rate of low-level driving assistance functions increases, advanced intelligent driving systems are at a turning point in development. In November last year, four ministries jointly issued a notice on the pilot work of intelligent connected vehicles’ access and on-road passage, specifying requirements for the access of L3/L4 automated driving and improving relevant rules. Domestic and foreign OEMs such as BYD, Changan, Zhiqi, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz, with strong L3 technology capabilities, actively applied for conditional automated driving test licenses on high-speed or high-speed roads. It is foreseeable that with more car companies joining in the development of L3 automated driving, advanced intelligent driving is expected to truly undergo a “qualitative change”. Currently, car companies mainly focus on NOA as the core driving force. At present, high-speed NOA has been mass-produced, and urban NOA is becoming the focus of competition among car companies, aiming to seize the initiative. Data shows that by 2023, there will be 940,000 vehicles equipped with navigation assistance driving. From 2023 to 2024, advanced intelligent driving functions represented by urban NOA will accelerate landing, with brands such as Huawei and Xiaopeng releasing advanced intelligent driving models one after another, and many OEMs launching landing plans.
Huawei is undoubtedly one of the most aggressive forces in intelligent driving. Currently, its urban NCA, which claims to be able to drive nationwide, has been launched. Xiaopeng’s XPILOT system has also entered the 4.0 stage, with its urban NGP covering 243 cities. By 2024, Xiaopeng’s XNGP will cover the national network of major cities, including internal roads, unnamed roads, and parking lots. Even Xiaomi, which has just released its first car model, is accelerating the expansion of urban NOA. Xiaomi Group Chairman and CEO Lei Jun introduced that the Xiaomi SU7 fully supports valet parking, parking in extremely narrow spaces, and high-speed navigation. Urban NOA will begin user testing in April, open in 10 cities in May, and achieve nationwide coverage in August. It is worth noting that the NOA function is mainly supported by autonomous mid-to-high-end models, with new energy brands mainly offering standard NOA function models. The penetration rate of Ideal and Aion is 100%. Among them, the highest proportion of models in the 350,000-400,000 price range, with a market share of 33.1%.
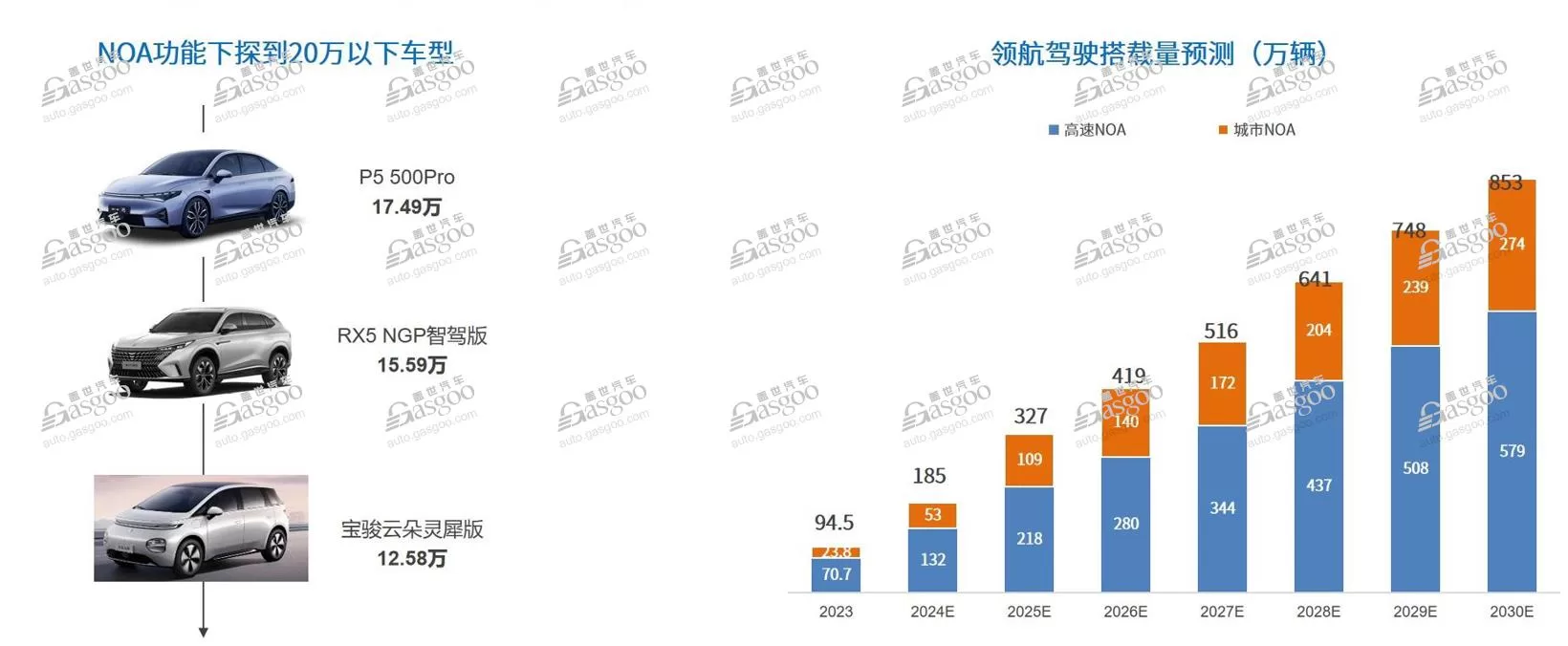
Currently, over 70% of vehicles equipped with NOA navigation function are priced above 300,000 yuan (41470$). However, we are starting to see the emergence of mid-to-low-end models such as Xiaopeng P5 and Baojun Cloud. The GAC Research Institute predicts that as vehicles equipped with navigation functions gradually reach the price range of around 150,000 yuan (20730$), the number of domestic NOA-equipped vehicles is expected to exceed 1.8 million by 2024, and the volume is expected to exceed 8.5 million by 2030.
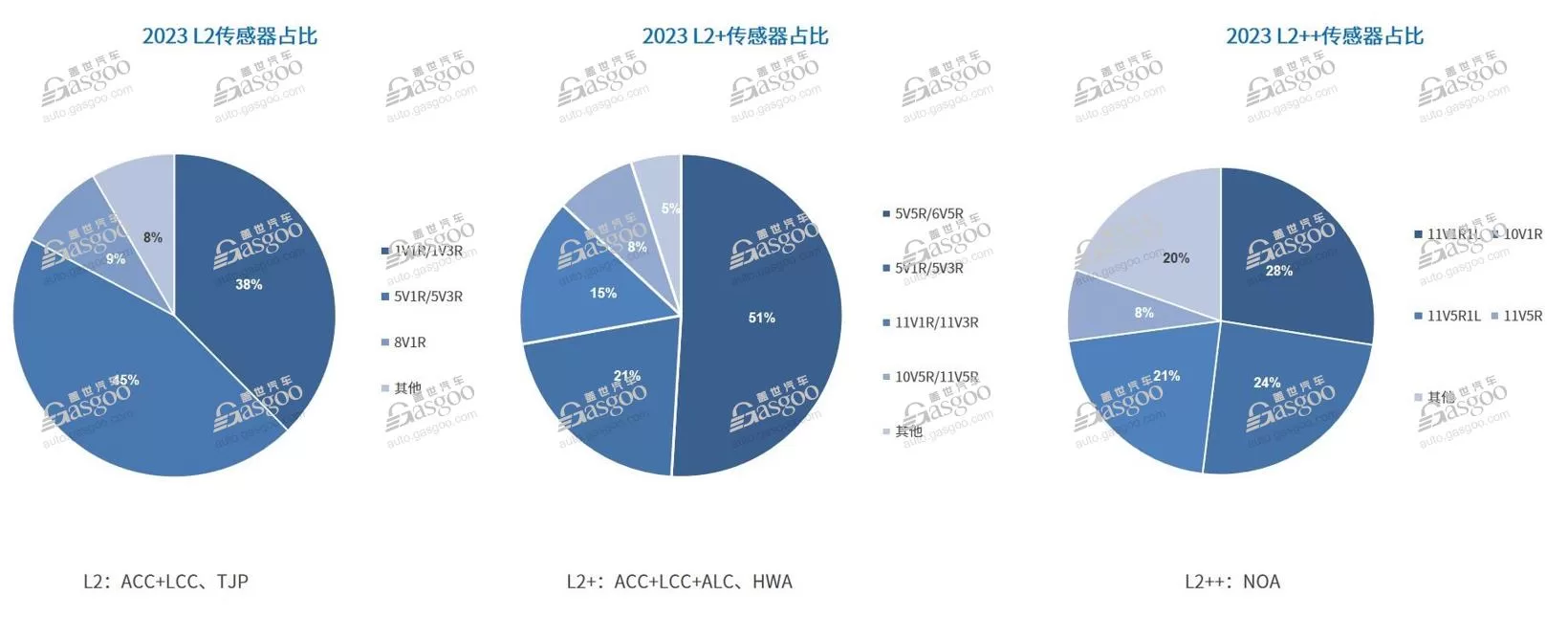
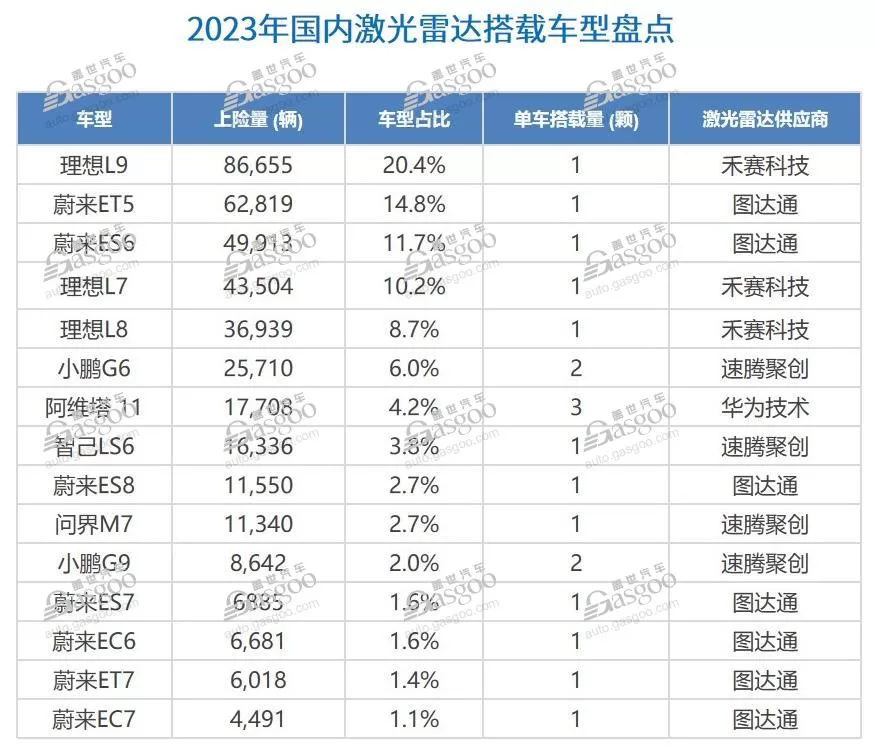
Heavy perception, light mapping remains mainstream, with rapid scaling period for LiDAR Urban NOA competition continues, focusing on achieving larger scale data collection at lower cost for algorithm optimization and model iteration. Price wars impact cost control for car manufacturers, leading to the prevalence of “heavy perception, light mapping” as a cost-effective solution. Car manufacturers aim to accelerate urban NOA expansion, with high costs and freshness issues of high-precision mapping hindering progress. Application of algorithms like BEV+Transformer enhances real-time perception on vehicles, reducing reliance on maps and making light mapping mainstream. In early February, WenJie launched the first batch of “No-Map NCA” push notifications, with an OTA update in March adding city smart driving assistance not reliant on high-precision maps, achieving “drive anywhere, as long as there’s a road” City NCA. Recently, ZhiJi Auto announced the start of “No-Map City NOA” public testing in Shenzhen, Guangzhou, and Suzhou in April, recruiting public testers. By mid-year, ZhiJi Auto will officially push IM AD No-Map City NOA. GaiShi Auto Research Institute believes that as autonomous driving algorithms mature, the future will focus on real-time perception + SD Pro maps/navigation maps as the main technical solution. LiDAR, a key sensor for enhancing vehicle perception, is gaining favor among car manufacturers. Data shows that by 2023, L2 level-equipped models mainly use 5V1R/5V3R sensor schemes, with most new vehicles featuring NOA adding LiDAR sensors to enhance vehicle perception.
Brands like Xiaopeng and Weimar have confirmed that LiDAR is a key sensor to ensure the comfort and safety of intelligent driving products. Since 2024, with the launch of models like Jike 001 and Zhi Ji L7, the trend of LiDAR becoming standard in the field of smart cars has become more obvious.
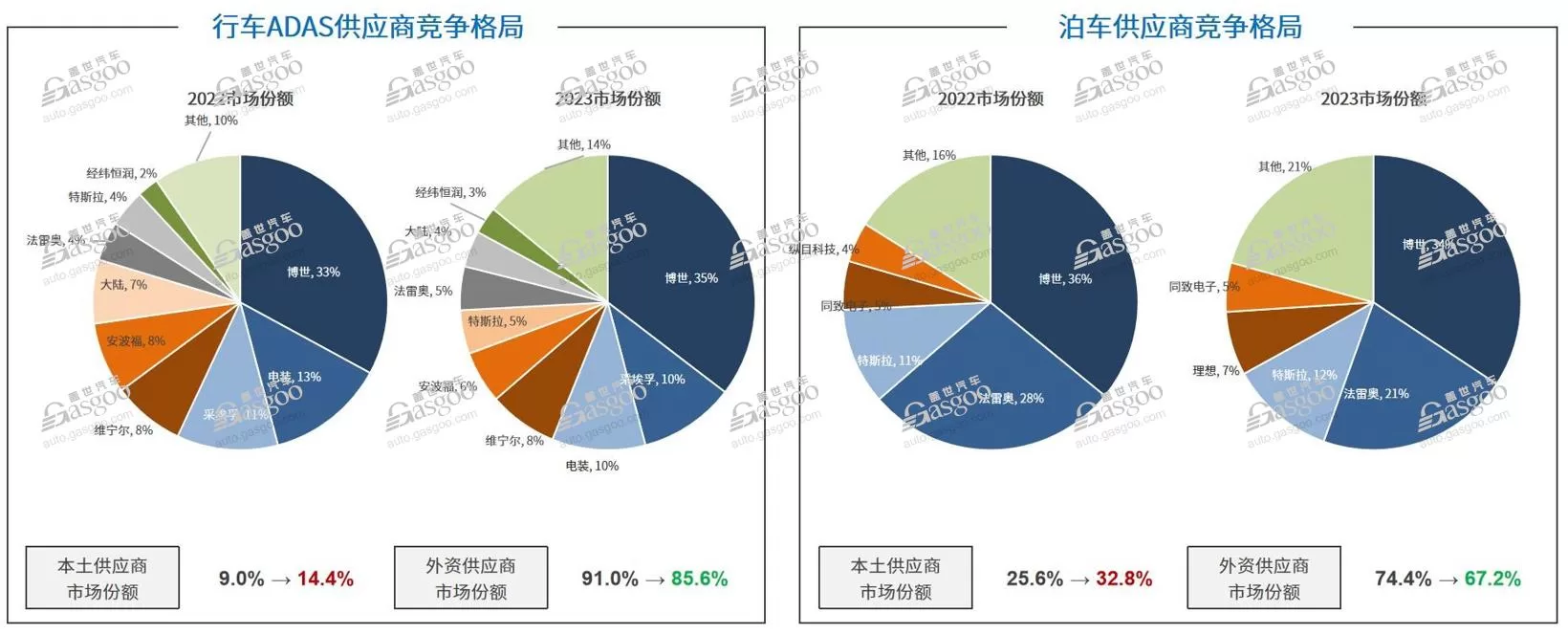
Competition in city NOA and the development of L3 and higher-level autonomous driving models are driving the rapid growth of LiDAR installations. LiDAR companies like Suteng Juchuang and Hesai Technology may have broader development opportunities. The smart driving supply chain is developing rapidly, with local players playing a key role. Among the various industry players, local manufacturers are gradually becoming a strong force. Currently, the advanced route of ADAS technology can be divided into driving and parking categories. Driving includes some active safety features, high-speed NOA, and city NOA; parking involves functions used in parking scenarios, such as memory parking and valet parking. In the past, foreign Tier 1 companies dominated the market share in driving ADAS and parking areas. However, in the past two years, with local suppliers entering the market from their own brands, their market share has been continuously increasing and is expected to further rise in the future. According to Gesi Automotive Research Institute, by 2023, the market share of local suppliers in the driving ADAS field will increase to 14.4%, while the market share of local suppliers in the parking field has exceeded 30%.
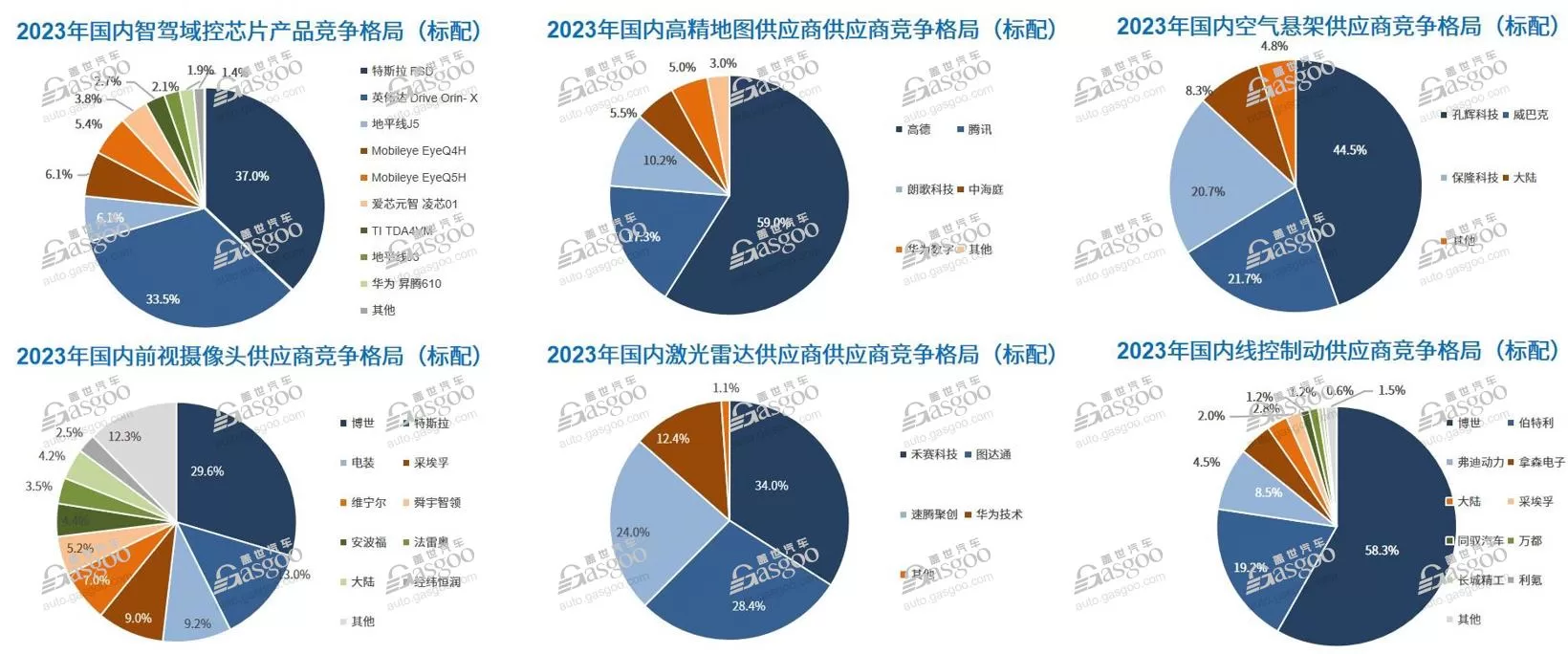
Integrated parking and driving is one of the important solutions in the current field of intelligent driving. Currently, the market share of integrated parking and driving, which is developed by OEMs and outsourced, is close to 50%. Local suppliers lead foreign Tier with advantages such as full-stack development capabilities, rapid product iteration, and multi-chip platform compatibility. Looking at components, besides LiDAR, some domestic suppliers stand out in areas such as air suspension, high-precision maps. In the field of intelligent driving domain control chips, wire-controlled actuators, some domestic companies have begun to achieve scale development.
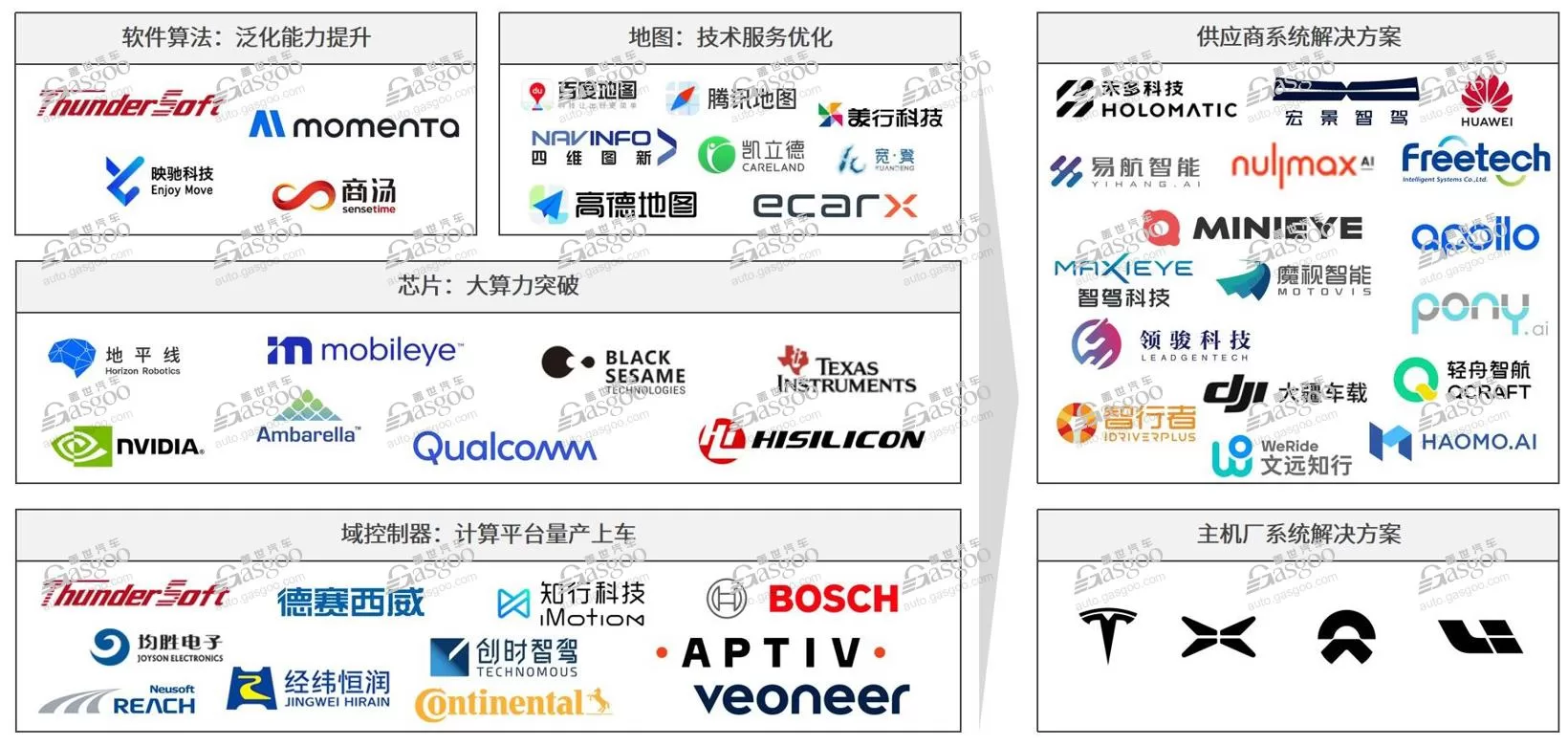
In relative terms, there is still a lot of room for growth in areas such as domestic cameras and millimeter wave radar. In the field of advanced intelligent driving, the domestic supply chain is developing rapidly, with many outstanding domestic manufacturers showing strengths in software algorithms, maps, chips, and overall solutions.
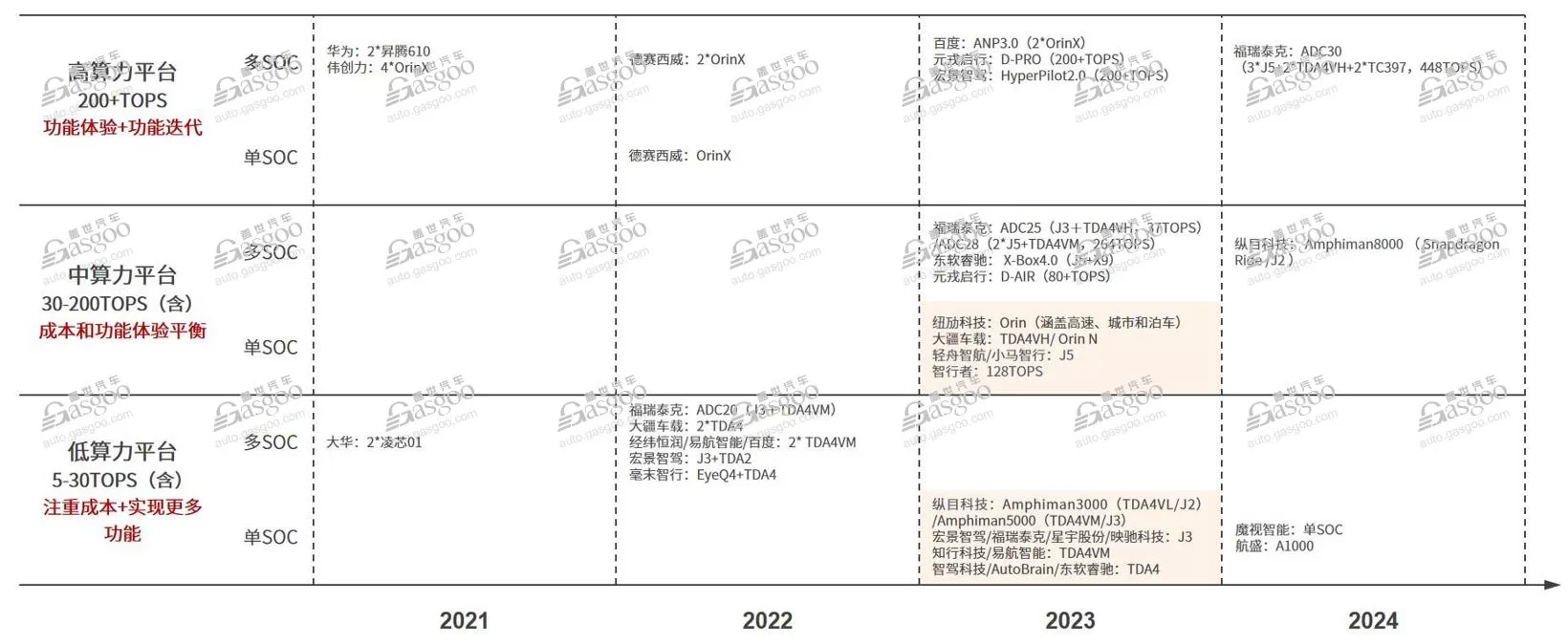
The mass production of NOA in the city has greatly driven the demand for upstream industries such as high-performance chips, LiDAR, and cloud services. Many suppliers have taken the path to going public as a result. On December 20th last year, Zhixing Technology, a major player in the domestic autonomous driving domain controller market, successfully listed on the main board of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. Earlier this year, TuSimple, a leading LiDAR company, made its debut on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, becoming the world’s largest LiDAR enterprise by market value. Many other smart driving companies are also planning IPOs. On March 28th, Horizon Robotics submitted its prospectus to the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, planning to list on the main board. As for car companies, given the current trend of intensified competition in the smart driving sector, independent car manufacturers are accelerating the research and application of intelligent driving technology. In terms of specific strategies, some major OEMs choose to independently develop to maintain technological leadership and independence. On the other hand, most car companies choose to cooperate with suppliers, directly purchasing mature solutions to reduce costs and achieve rapid deployment. Currently, suppliers providing smart driving solutions in the market include automotive parts giants, tech giants, and specialized startups, forming a diverse force for the development of smart driving. With ongoing investment in technology research and development by independent car companies and the expansion of market share by domestic suppliers, the two are mutually reinforcing, providing strong support for the rapid development of smart driving technology. In the future, this trend is expected to continue strengthening, further driving the popularization and application of intelligent driving technology in the Chinese and global markets. Cockpit integration is gradually being mass-produced, and autonomous driving is moving towards end-to-end. When discussing the future of intelligent driving, key words such as cockpit integration, high computing power chips, large models, and end-to-end cannot be avoided. The concepts of driving and parking integration are gradually maturing, ultimately leading to cockpit-driving integration or cockpit-driving integration. The electronic/electrical architecture of vehicle manufacturers is upgrading to domain-centralized architecture, with driving and parking sensors and domain controllers sharing technology becoming increasingly mature. The development of cockpit integration technology is in an active transitional period, with both vehicle manufacturers and suppliers laying out the cockpit integration domain control. Some companies have introduced related products, such as Bosch’s central computing platform and Changxing Zhijia’s cockpit integration platform. It is expected that by 2024, cockpit integration domain control will achieve small-scale production, and with the maturity of technology and market demand, it may be widely used in the near future. High computing power chips are crucial for achieving cockpit integration, supporting increasingly complex algorithms and processing large amounts of data, ensuring system security and reliability. However, based on the technology of integrated parking and driving, which is one of the main focuses of intelligent driving at present, most of the low and medium computing power integrated parking and driving solutions currently on board adopt a multi-SOC solution. On the new generation platform, a single-SOC solution is adopted. Due to the need to support higher-level intelligent driving functions, the high-computing integrated parking and driving domain controller mainly adopts a multi-SOC solution, considering issues such as immature computing power embedding and system redundancy.
With the improvement of AI algorithms and chip design capabilities, even low-power SOC platforms can provide enough performance to support basic functions of autonomous driving. Cost-effective single SOC low-power platforms are expected to lead the way. Another crucial factor is the iterative innovation of autonomous driving algorithms. Many top car companies choose to follow Tesla’s algorithm iteration method, mainly in three stages: First stage: Tesla introduced BEV and Transformer technology in its autonomous driving system, achieving “map-free” and marking the application of large models in onboard systems; Second stage: upgrade network occupancy to achieve “laser-free”; Third stage: end-to-end autonomous driving.
On March 18th this year, Tesla began rolling out FSDV12.3 in North America, introducing “end-to-end neural network” technology, sparking industry discussions once again. The current intelligent driving system uses a modular model, dividing perception, prediction, and planning into three separate modules with significant technical differences. This modular architecture may lead to information loss during information transmission, making the system complex and difficult to maintain, unable to effectively handle complex road environments. In contrast, end-to-end models have clear advantages in intelligent driving solutions, integrating perception, prediction, and planning into a single model, simplifying the structure of the solution and improving computational efficiency. Compared to traditional rule-based models, end-to-end models are easier to scale and achieve performance breakthroughs. However, the drawbacks of end-to-end models are also evident. End-to-end models are often seen as “black boxes,” merging multiple steps into one model, making it more difficult to understand how the model works internally. This lack of transparency may lead to issues with interpretability and explainability. Additionally, end-to-end models require more computational resources, significantly increasing the cost and time for training and deploying the model. Furthermore, end-to-end models may face challenges in debugging, optimization, and overfitting. Nevertheless, many companies believe that despite these drawbacks, end-to-end autonomous driving is one of the most promising paths to achieve driverless vehicles in the future. Companies like WeRide, DeepRoute, and others have chosen to follow Tesla’s technological path, deepening their exploration on this road. Currently, the autonomous driving industry is at a turning point, and exciting innovations and advancements may be seen in the coming years.