Global agencies project that in March 2024, global sales of light vehicles will reach 8 million units, a 2% increase compared to the previous year. Cumulative sales from the beginning of the year have grown by over 4%. However, the annual sales rate for light vehicles worldwide stands at 85 million units, remaining steady compared to February but still weaker than the second half of last year. Global car market in March: China and the US lead, Europe declines by 2.8%.
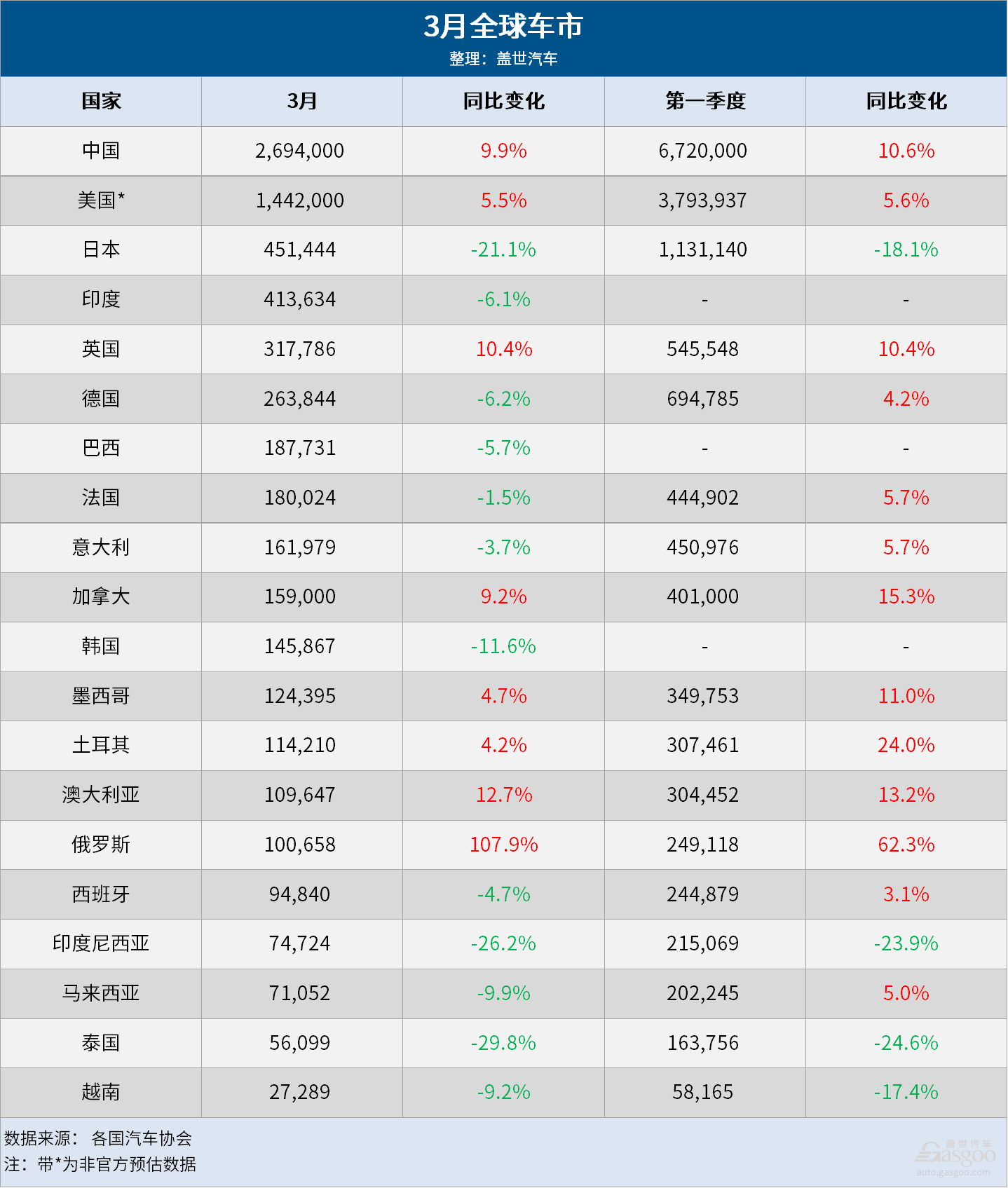
In March, China’s automobile production and sales were 2.687 million and 2.694 million, up 78.4% and 70.2% respectively compared to the previous month, and up 4% and 9.9% year-on-year. In the first quarter, China’s cumulative automobile production and sales were 6.606 million and 6.72 million, up 6.4% and 10.6% year-on-year, achieving a strong start to the year and hitting a new high since 2019. Chen Shihua, Deputy Secretary General of the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, said that after the Spring Festival, many new cars were launched, offline activities such as car shows and car promotions in rural areas were gradually carried out, and some regions introduced “trade-in” promotion policies, driving rapid growth in car sales compared to the previous month and year. He also pointed out that currently, exports are an important growth area, while insufficient domestic demand is a key issue to be addressed this year. Chen Shihua also stated, “In 2024, the domestic automobile growth rate is likely to show a trend of high growth followed by low growth. Before the introduction of the ‘trade-in’ policy, the total annual sales of the domestic car market in 2024 may be similar to last year, but after the policy is introduced and implemented, the overall domestic car market will see significant growth.” Benefiting from increased inventory, healthy growth in fleet sales, and significantly increased incentive measures stimulating retail demand, the U.S. automobile market also maintained a growth trend of over 5% in March and the first quarter. In March, U.S. light vehicle sales are expected to be 1.44 million, up 5.5% year-on-year, marking the 20th consecutive month of growth. Analysts point out that rising borrowing costs and increased new car prices are dragging down the market, leading many consumers to instead purchase smaller, cheaper cars. Jessica Caldwell, sales and insights director at Edmunds, says price is key in this high-interest rate era. Consumers focus on monthly payments. Offering competitive prices for attractive car products will lead to the most success for car manufacturers. David Oakley, Americas automotive sales forecast manager at GlobalData, notes that lower-priced car markets perform well. Demand for higher-priced models is slowing. Sales of major manufacturers vary. Some brands are falling behind due to aging product lineups and/or lack of incentives. April’s sales situation will be worth watching, given the relatively strong sales a year ago. In March, new car registrations in Europe reached 1.38 million, a 2.8% year-on-year decrease. This is the second consecutive month of decline in four months, mainly due to weak demand and the impact of Easter. Except for the UK, sales in Germany, Spain, Italy, and France have all declined, with Norway hitting its lowest level in 15 years. The decline in new car sales in Europe in March highlights the pressure facing car manufacturers as interest rates rise, economic growth slows, and subsidies to stimulate demand for electric cars gradually decline. However, thanks to a more favorable supply environment, GlobalData predicts that passenger car sales in Western Europe will exceed 12 million units in 2024, the strongest annual sales performance since the COVID-19 pandemic. In March, new car sales in Japan reached 451,444 units, a 21% year-on-year decrease. In the first quarter, Japan’s total new car sales reached 1,131,140 units, a decrease of 18% since Daihatsu announced the suspension of production at the end of last December due to a safety testing scandal. Toyota, Mazda, and Subaru have been affected. Although Daihatsu has resumed delivery of some models, uncertainty remains. However, there are some positive signs in the Japanese car market. The Bank of Japan ended its negative interest rate policy in March, and with recent wage increases across Japan, household spending is expected to rise. In March, South Korea’s overall car market sales dropped by 11.6% year-on-year. The sales of the top five car manufacturers in South Korea plummeted by 15%, largely due to Hyundai’s factory maintenance and production line maintenance shutdown, as well as a reduction in working days during the New Year holidays. However, South Korea’s imported car sales reversed the downward trend of the previous two months, increasing by 6% year-on-year to 25,263 units. However, the Bank of Korea has significantly raised interest rates from 0.5% to 3.5% in recent years, putting increasing pressure on debt-ridden South Korean consumers. Overall, excluding factors such as holidays, the global light vehicle market started off well in 2024. However, the global car market still faces many challenges: rising interest rates, tightening affordability, supply chain uncertainties, and ongoing “growing pains” of electrification. Analyst Colin Couchman said: “We are cautious about the recovery of the global car market in 2024. The automotive industry will move away from obvious supply-side risks and enter a more ambiguous macroeconomic demand environment.” 1. Global light vehicle sales in 2024 are expected to reach 92.4 million units, up 2% from the previous year. 2. In March, the new energy vehicle market saw a 35% surge in China, while Europe experienced a 7.4% decline.
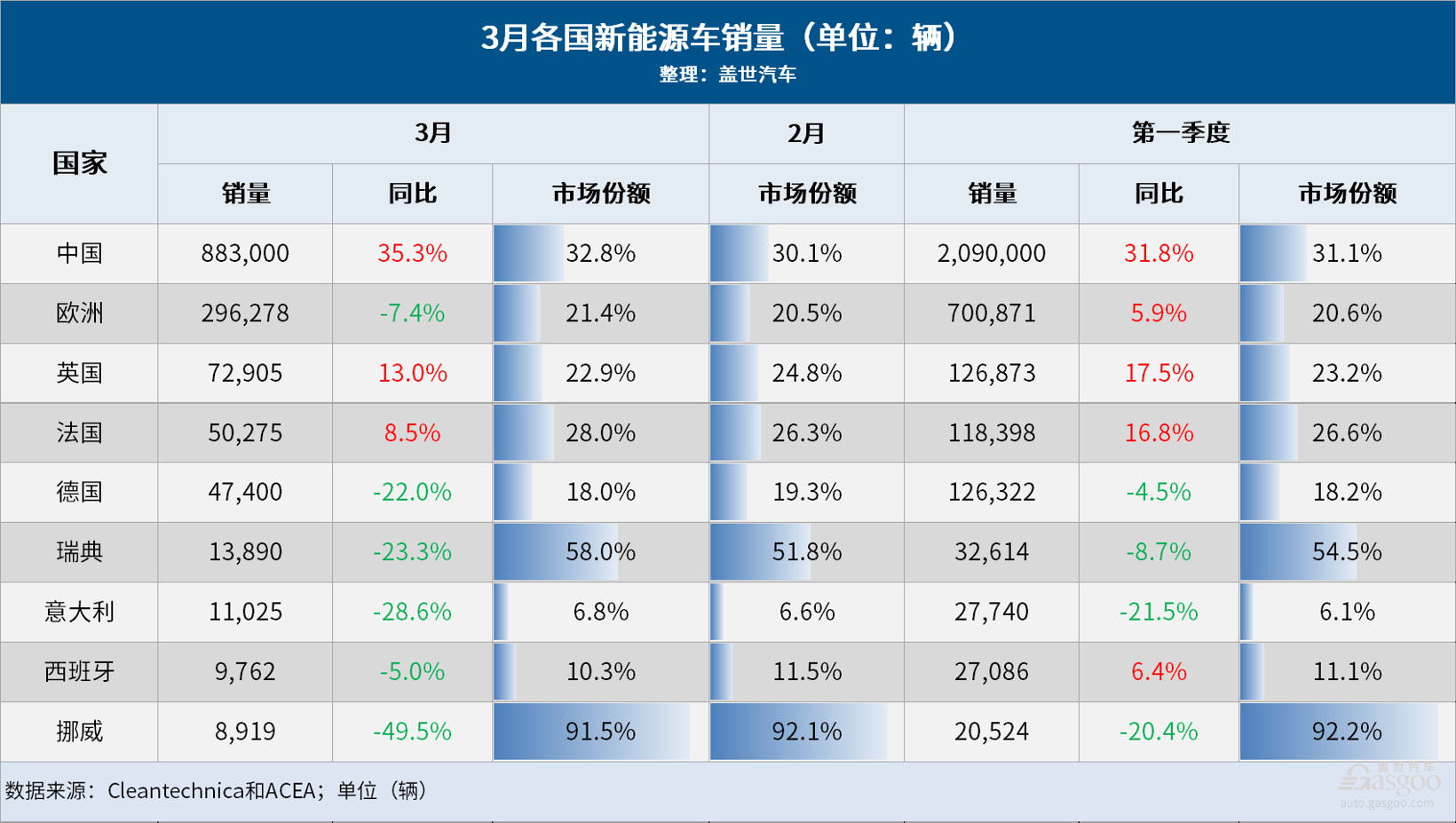
Market research firm Rho Motion forecasts global electric vehicle sales to reach 1.23 million in March 2024, up 12% year-on-year. Specifically, the company predicts a 27% increase in electric vehicle sales in China, a 15% increase in the United States and Canada, but a 9% decline in Europe. Rho Motion believes that growth in the Chinese and American markets offsets the decline in the European market. As consumers wait for more affordable electric vehicle models to hit the market, demand for electric vehicles has cooled in recent months. However, Rho Motion data manager Charles Lester states, “Overall, global electric vehicle sales growth has slowed, but there are still some positive factors.” In March, China’s production and sales of new energy vehicles reached 863,000 and 883,000 respectively, up 28.1% and 35.3% year-on-year, with a market share of 32.8%. In the first quarter, China’s production and sales of new energy vehicles reached 2.115 million and 2.09 million respectively, up 28.2% and 31.8% year-on-year, with a market share of 31.1%. Luo Lei, assistant chairman of the China Automobile Dealers Association, stated, “Looking at the data from March, the overall penetration rate of new energy vehicles reached 41%, and in the first half of April, the penetration rate exceeded 50%. It is expected that the annual penetration rate of new energy vehicles in the market will exceed 40%.” Currently, China’s new energy vehicle industry is in a period of rapid growth with enormous potential. Meanwhile, the situation in the European electric vehicle market is not optimistic, with sales declining by 7.4%. Due to reduced demand in Germany, Sweden, and Norway, pure electric vehicle sales in Europe in March fell by 11% year-on-year. Specifically, Italy and Germany saw their pure electric vehicle sales decline by 34% and 29% respectively. Italian consumers are expecting the government to introduce new subsidy policies, leading to a delay in purchasing electric vehicles. The German government canceled subsidies for electric cars last year, and subsidies from car companies were not enough. Market demand is weak, incentive measures have been canceled, range anxiety, uncertain economic outlook, and lack of affordable models limit further popularization of electric cars in Europe. The market in 2024 will be difficult due to weak global demand for electric cars, increased competition from Chinese rivals, cost pressures, and geopolitical tensions. As the largest car market in Europe, Germany saw a 22% year-on-year decrease in electric car sales in March, with a market share of 18.0%, still affected by the sudden cancellation of subsidies at the end of December. Pure electric car sales in Germany were 31,384 units, a decrease of about 29% year-on-year, with a market share of 11.9%; plug-in hybrid car sales decreased by 4.5%, with a market share of 6.1%. Germany’s economy is in recession, with a consumer confidence index of -27.4, still very negative. Data shows that low-priced pure electric cars in Germany are priced too high, coupled with widespread economic recession and the cancellation of subsidy policies, leading to a year-on-year decline in pure electric car sales in Germany, and the market share of pure electric cars in the German car market is also shrinking. Meanwhile, European automakers are achieving record profits. As the fastest-growing market for electrification in Europe, Norway’s electric car market share in March reached 91.5%, higher than the same period last year’s 91.1%, with pure electric cars alone accounting for nearly 90% of the market share, while plug-in hybrid cars accounted for 2.2%. The Tesla Model Y once again became the best-selling car in Norway, ranking first for the eighth consecutive month, with its March sales almost equaling the total of the following 7 pure electric cars. The overall decline in the Norwegian car market and pure electric car sales may reflect the continued weakness of the overall economy, with negative consumer and business confidence. The Norwegian Road Traffic Information Council also believes that the sharp drop in sales should be blamed on economic conditions. “New car sales are usually an indicator of people’s financial situation, reflecting the financial challenges many are facing…” OFV also stated: “Compared to the past five or six years, most people are now choosing smaller, more affordable new cars… This will affect future new car sales… Many major car manufacturers are now seeing the huge potential of small, affordable electric cars and are shifting some production in that direction. In the future, there will be many smaller, more affordable new electric cars on the Norwegian market.” The International Energy Agency predicts that although some markets are facing economic challenges, global electric car sales will reach 17 million units in 2024, higher than the 14 million units in 2023. The International Energy Agency pointed out, “Thin profit margins, fluctuating battery metal prices, high inflation, and some countries gradually phasing out purchase subsidies have raised concerns about the growth rate of the electric car industry, but global sales data remains strong.” Price remains the key to growth in the electric car industry compared to traditional cars, with significant price differences in different regions. As JATO said in a report released in October last year, “Consumers in Europe need to spend at least 18,285 euros to buy a pure electric car, while in the United States they need to spend at least 24,400 euros, which is 92% and 146% more expensive than the cheapest fuel cars.” “This is largely because the automotive industry continues to focus on high-end electric cars rather than more affordable mid-range cars. Many Western car manufacturers have raised prices, forcing consumers to wait longer to buy new cars. This strategy has paid off for many OEMs. In 2022, most car manufacturers saw a decrease in sales, but revenue increased, and profits reached record levels.” The International Energy Agency believes that price and charging infrastructure will be key to the future growth of the electric car market. In the future, lowering electric car prices and improving charging infrastructure should remain top priorities for the automotive industry to achieve green transformation.