“Parking space to parking space” is becoming the benchmark for end-to-end technology. “Future cars without advanced intelligent driving will lack competitiveness,” many industry experts recently told Gaishi Automotive. From automated parking to fully autonomous driving, intelligent driving now serves as a key standard for assessing a new car’s advancement and appeal. Major automakers must increase their investment in intelligent driving research and development. As the Guangzhou Auto Show unfolds, the latest technologies and trends in the automotive industry converge. Automakers showcase their innovations. Competition in advanced intelligent driving technology intensifies, with keywords like end-to-end and parking space to parking space taking center stage. Li Auto presented its latest intelligent driving technology—an end-to-end + VLM dual system. At the same time, Li Auto officially launched its parking space to parking space intelligent driving feature. With the attention generated by the Guangzhou Auto Show, Li Auto recently held an end-to-end intelligent driving experience day. To better understand the practical application of this technology, Gaishi Automotive conducted a real-world test of Li Auto’s parking space to parking space capability enhanced by the “end-to-end + VLM” system.
“Parking to Parking” Function Tested We chose a route with various road conditions. It included narrow city streets, congested areas, roundabouts, highways, and internal roads in a park. Users input the destination parking information in the vehicle’s system. The vehicle automatically plans the route and guides the user. Upon arrival, the vehicle recognizes and parks in the designated spot. After selecting the navigation route, users click “One-Key Smart Drive” or activate it with voice commands. The parking-to-parking process starts immediately. The vehicle exits parking spaces, garages, and narrow community roads smoothly. It stops automatically at barriers and resumes after payment. Ideal Auto states that this function supports outdoor parking lots, internal parks, multi-story garages, and automated parking systems. Once on public roads, the smart driving system handles roundabouts, U-turns, and construction scenarios well. It navigates complex traffic situations and traffic lights smoothly.
The technology behind this supports Ideal’s intelligent driving solution, which combines end-to-end and VLM systems. End-to-end does not rely on rule-based logic. It offers a more human-like driving style. VLM understands complex traffic environments and Chinese semantics, enhancing the vehicle’s navigation capabilities. For the U-turn function, Ideal Auto told Gaishi Auto that end-to-end uses human driver data. It can generate a reasonable trajectory in various U-turn scenarios. It no longer relies heavily on navigation information and the topology of adjacent lanes. Additionally, end-to-end has stronger lateral perception. During a U-turn, it can accurately identify and predict the trajectories of oncoming vehicles and take evasive action.
Li Auto’s ETC system at highway toll stations stands out. It connects urban and highway driving scenarios. According to Li Auto, this feature has no restrictions. Users nationwide can access it without any learning curve.
Ideal Auto stated, “The end-to-end + VLM architecture allows the system to drive like a human. It also understands complex semantic information in the real world. In the scenario of autonomous ETC passage, VLM identifies toll booths and ETC lane positions. It guides the end-to-end system to the ETC lane and through the gate.” The system also features roadside starts and roundabout navigation. Despite poor weather and complex road conditions, Ideal Auto’s intelligent driving system maintained high stability and accuracy throughout the journey. It successfully parked in the designated space.
Currently, Li Auto has launched the end-to-end + VLM parking feature. It has begun testing with thousands of users and nationwide stores. By the end of November, it will push this feature to AD Max users with the OTA 6.5 version. In the past year, Li Auto’s smart driving technology has rapidly developed. It achieved full-scenario NOA capabilities, launched no-map NOA, and integrated end-to-end with VLM technology. This process marked three generations of technological iteration. Li Auto’s position and role in smart driving have changed. Li Auto’s success stems from its innovative strategy. It uses a dual-system architecture that combines end-to-end and VLM.
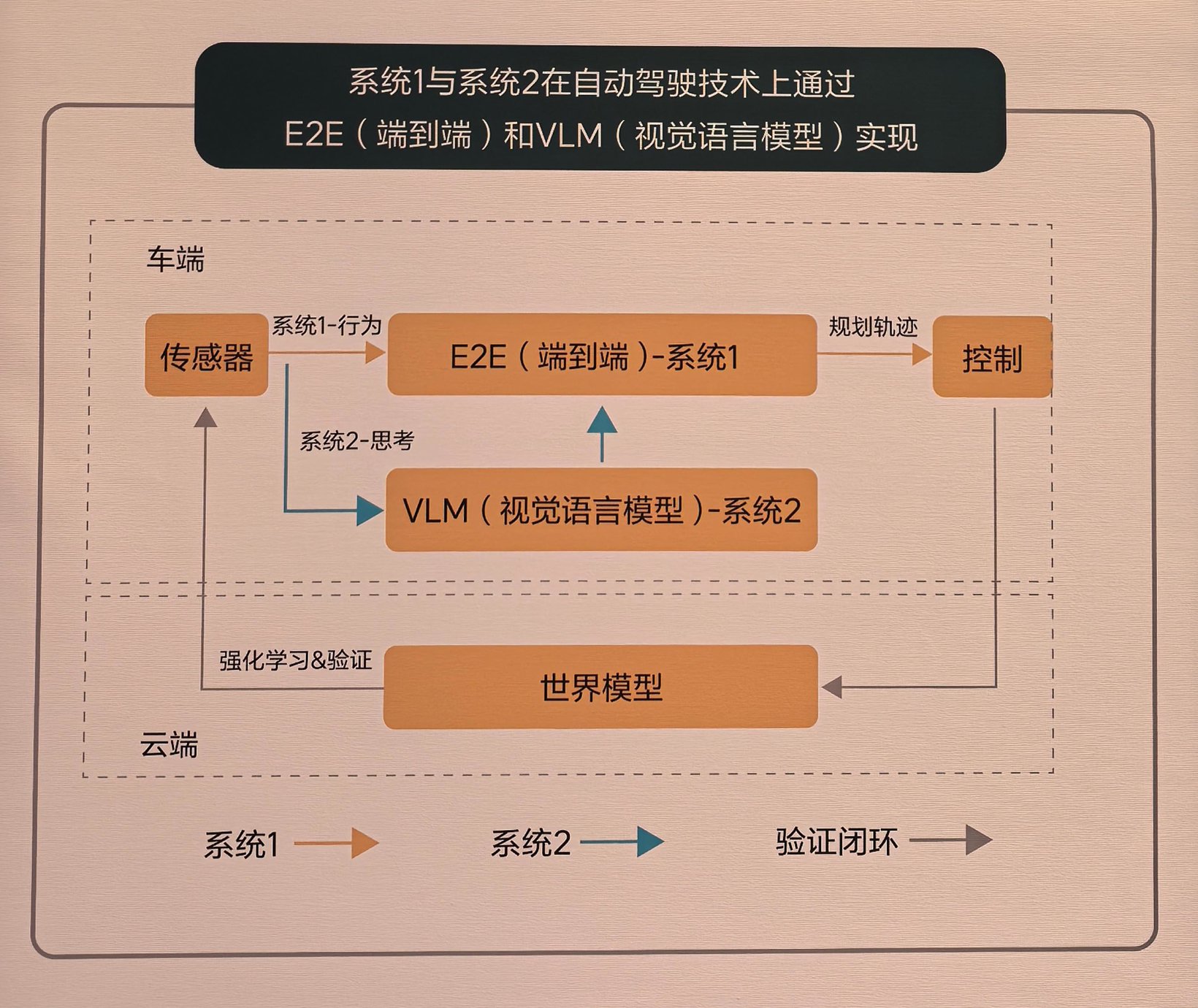
Ideal Auto introduces its approach based on Daniel Kahneman’s theory of two thinking systems from “Thinking, Fast and Slow.” It merges the end-to-end system with a visual language model for autonomous driving technology. This aims to enhance the vehicle model’s performance and development potential. System 1, the end-to-end model, operates as an intuitive and quick-response mechanism. It maps sensor inputs directly to driving trajectory outputs without intermediate steps. It represents an integrated One Model.
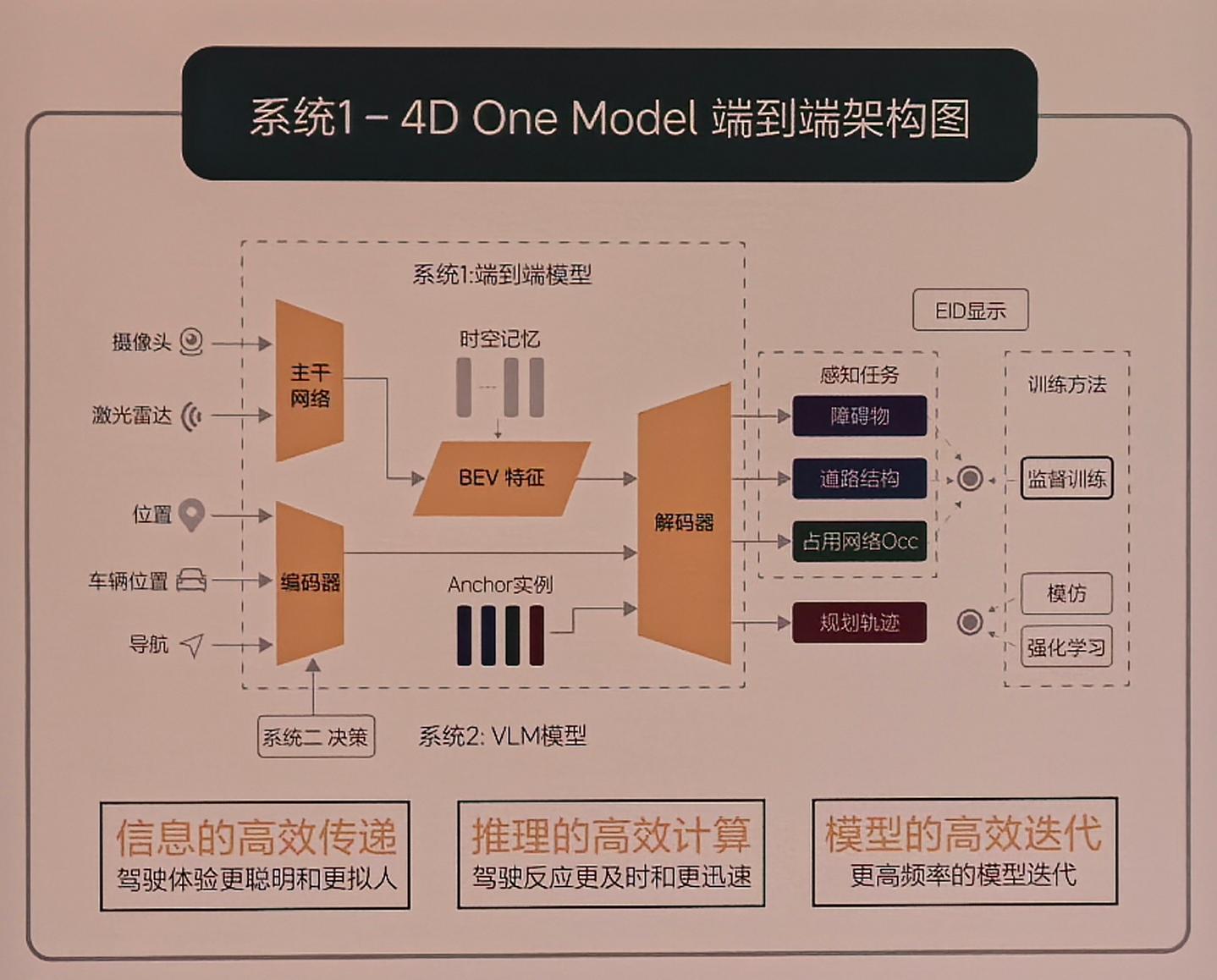
This design ensures efficient information transfer, effective reasoning, and rapid model iteration. System 1 uses an end-to-end model. Its input includes cameras and LiDAR. A convolutional neural network, optimized for the NVIDIA Orin-X, extracts and fuses multi-sensor features. It projects these features into BEV space. To enhance representation, Ideal designed a memory module. This module includes both temporal and spatial memory. Besides cameras and LiDAR, Ideal added vehicle state information and navigation data to the model’s input. After encoding with a Transformer, the model decodes dynamic obstacles, road structures, and general obstructions, then plans driving trajectories. System 2 operates with a 2.2 billion parameter visual language model. Its output integrates with System 1 to form the final driving decision.
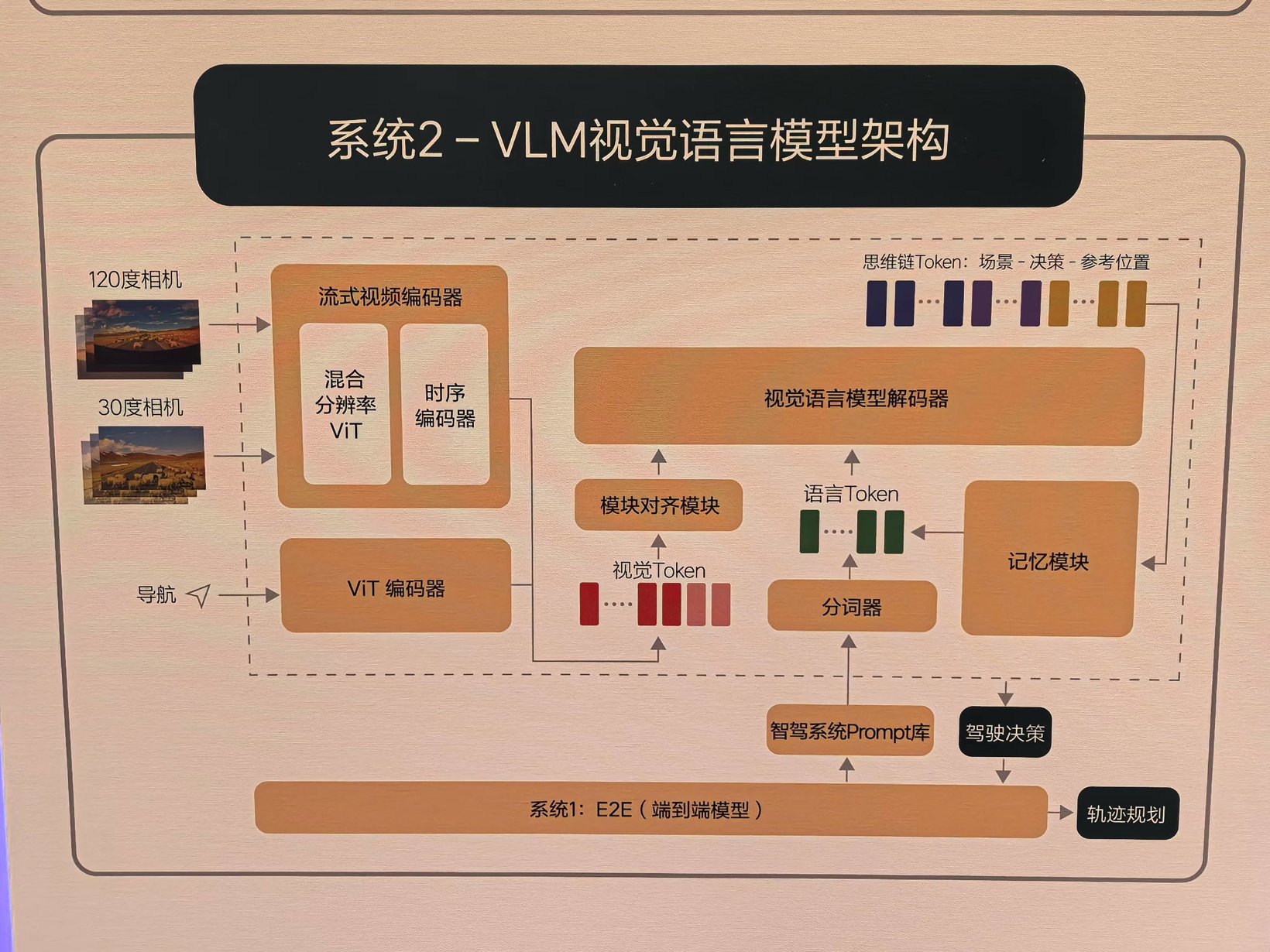
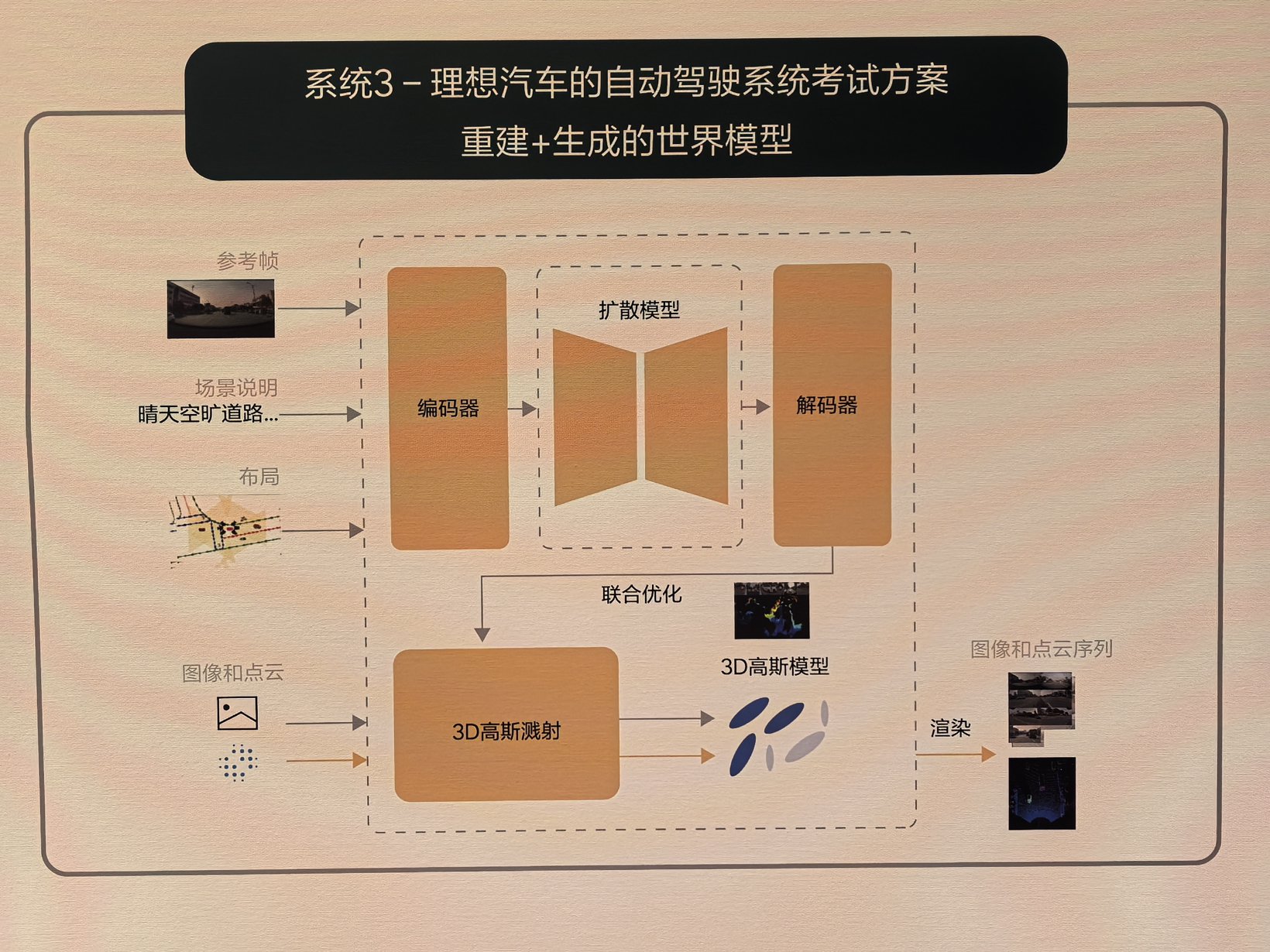
The overall algorithm architecture of VLM consists of a unified Transformer model. It tokenizes the prompt text. It encodes images from 120-degree and 30-degree cameras along with navigation map information. The model aligns modalities through a text-image alignment module. It then feeds the data into the Transformer model for autoregressive inference. Additionally, Ideal uses a cloud-based world model to train and test the capabilities of System 1 and System 2. This approach enables rapid iteration of the system.
Ideal aims to deploy visual language models on vehicle chips. This will help autonomous driving understand complex traffic environments and Chinese semantics, similar to human comprehension. It will also assist in addressing safety, navigation, regulations, and comfort issues in the industry. The end-to-end + VLM architecture gains popularity among automakers and intelligent driving suppliers. However, its application in autonomous driving faces many challenges. Not everyone can navigate these complexities. Currently, both end-to-end models and VLM require large amounts of high-quality training data. Obtaining and labeling this data is time-consuming and costly. It is crucial to ensure data diversity and representation to cover various driving scenarios and conditions. Additionally, data processing and storage present challenges, necessitating efficient algorithms and hardware support. The complexity of the end-to-end + VLM model increases R&D costs and raises demands on vehicle computing power. As a reference, Ideal’s intelligent driving has accumulated 2.67 billion kilometers. Its training power currently reaches 6.83 EFLOPS and is expected to exceed 10 EFLOPS by year-end. The extensive mileage, growing training power, and early deployment of world models in the cloud enable rapid iteration of Ideal’s end-to-end + VLM intelligent driving system. The competition among leading intelligent driving companies intensifies. End-to-end has become a watershed for corporate capabilities. The focus shifts from technical disputes to practical experiences. Among these experiences, one core application is parking space to parking space. Wen Zhiyu, head of intelligent driving technology planning at Ideal, stated in an interview that the past two years focused on implementing various intelligent driving scenarios, such as highway NOA and urban NOA. “When we try to connect these scenarios, we find that some previous ideas can address certain gaps. However, the solutions are not always ‘elegant’ or efficient for generalized national scenarios.” This is one reason why Ideal and the industry pay more attention to end-to-end and “parking space to parking space” solutions. The “parking space to parking space” feature requires the autonomous driving system to navigate from a designated starting space to a target space. It must handle various complex traffic situations and obstacles. Implementing this feature poses a significant challenge for existing smart driving systems. The systems need high environmental perception, decision-making, planning, and execution capabilities. End-to-end technology plays a crucial role in the parking space to parking space application. This technology allows vehicles to autonomously judge and plan their driving trajectory through real-time perception of the surrounding environment and obstacles, without a preset route. It enables automatic parking and maneuvering in and out of spaces. This makes vehicle operation in parking lots more human-like, adapting better to complex environmental changes. At the Guangzhou Auto Show, several car manufacturers showcased their end-to-end parking space to parking space capabilities. Xiaopeng Motors announced it became the first company in the industry to achieve “parking space to parking space” with its Xiaopeng Turing AI smart driving system. Xiaopeng’s solution integrates scenarios like basements, gates, and urban roads using a single software logic. It plans to fully launch this on AI Tianji 5.5.0 in the future. Xiaomi also demonstrated its “parking space to parking space” smart driving capability at the Guangzhou Auto Show. According to Xiaomi’s plan, it will begin targeted internal testing for this feature starting November 16. By the end of December, it will launch a pioneer version. Xiaomi explained that the route establishment process for the upcoming “parking space to parking space” feature fully automates map and path creation in the background. For example, for commuting routes, users only need to drive in and out of the parking lot once, without any additional guidance. The system will automatically create the parking lot map in the background. ZEEKR also announced its D2D parking space to parking space navigation assistance feature, expected to be rolled out in batches around January 2025. The “parking space to parking space” feature is becoming a key metric for assessing end-to-end performance. It has become a litmus test for evaluating the smart driving capabilities of car manufacturers. Recently, many companies have announced their entry into the first tier of smart driving. This group is growing increasingly crowded, with players showcasing their strengths, such as Xiaopeng’s cloud model, NIO’s NWM world model, and Li Auto’s end-to-end + VLM dual system solution. In the new round of end-to-end smart driving competition, the industry landscape remains unstable. We are far from stability.